What are the basics of RFID?
Do you know the basics of RFID?
What is RFID you ask? Below is a quick little tutorial I’ve put together to explain the basics of RFID.
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. These labeling systems are becoming ever more popular and expanding across all market sectors and applications, including health care, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, transportation and retail. Many companies have started to mandate their suppliers to start utilizing RFID technology as part of supply chain compliance programs.
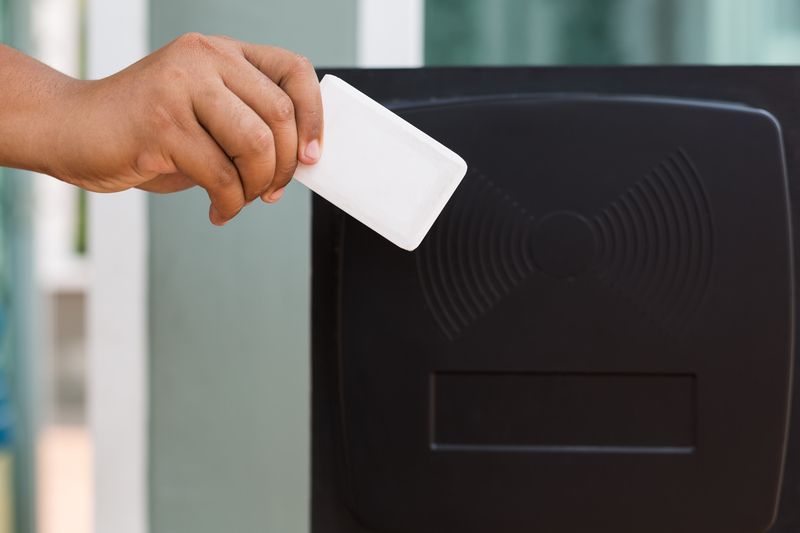
A RFID system consists of the following components:
- A programmable RFID tag which stores the data. Within this tag contains a RFID chip and an antenna to facilitate communication with the RFID chip via radio frequencies.
- A reader/antenna system
Types of RFID tags:
- Passive – are powered from the signal carried by the RFID reader. They do not have an integrated power source.
- Active – have a built-in power source and therefore can operate at greater distances and higher data rates. Active tags cost more compared to passive tags.
Factors determining the performance characteristics of the RFID tag:
- the type of IC used
- the read/write capability
- the radio frequency
- power settings
- environment
RFID systems are designed to operate at the following frequencies:
- Low Frequency (125kHz) – used for access control, security, manufacturing, animal identification
- High Frequency (13.56MHz) – used in library tracking, healthcare patient identification, access control,
Ultra High Frequency (860-960MHz) – used in supply chain tracking - Microwave (2.45GHz) – used in active RFID systems such as railroad car tracking, container tracking, automated toll collection
Benefits of RFID Technology over standard barcode identification:
- Information stored on the tag can be updated on demand
- Large data storage capacity
- High read rates
- Ability to collect data from multiple tags at a time
- Data collection without line-of-sight requirements
- Longer read range
- Greater reliability in harsh environments
- Greater accuracy in data retrieval and reduced error rate
Drawbacks:
- Higher unit cost than a regular barcode label. A typical barcode label costs about $0.02, whereas an RFID tag label can costs upwards of $0.10 or more depending on quantity.
- Higher initial implementation costs for RFID are also higher, depending on requirements and equipment specifications.
- However, these are off set in the long-term with the competitive advantages of RFID
For further information on RFID and to learn more about your options on your barcoding and labeling needs, call us as (800) 643-2664 and immediately talk to one of our friendly representatives; or chat us up on Facebook , Twitter , Google+ and LinkedIn !